Click here to watch in Youtube :
Click the below Image to Enlarge
 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java Serialization with IS A Inheritance) |
import java.io.Serializable;
/*
* If a class implements serializable then all its sub
* classes will also be serializable.
*/
public class Person implements Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7438582605700356851L;
protected String name;
protected int age;
public Person(String name, int age)
{
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
}
/*
* We can serialize the Employee class object that
* extends the Person class which is Serializable.Parent
* class properties are inherited to subclasses so if
* parent class is Serializable, subclass would also be.
*/
public class Employee extends Person
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 312396230370712755L;
private int salary;
public Employee(String name, int age, int salary)
{
super(name, age);
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary)
{
this.salary = salary;
}
}
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class SerializationDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
SerializationDemo serializationDemo = new SerializationDemo();
serializationDemo.writeEmployeeObject();
}
private void writeEmployeeObject() throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException
{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
try
{
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("employee.tmp");
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
Employee employee = new Employee("Peter", 29, 80000);
/*
* Write the specified object to the
* ObjectOutputStream.
*/
objectOutputStream.writeObject(employee);
System.out
.println("Successfully written employee object to the file.\n");
}
finally
{
if (objectOutputStream != null)
{
/*
* Closing a ObjectOutputStream will also
* close the OutputStream instance to which
* the ObjectOutputStream is writing.
*/
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
}
}
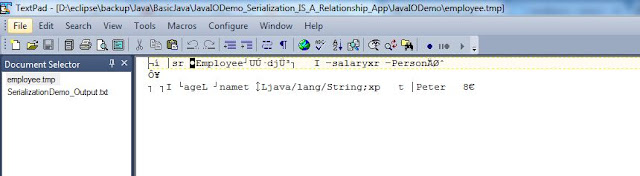
Successfully written employee object to the file.
employee.tmp
DeSerializationDemo.java
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class DeSerializationDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
DeSerializationDemo deSerializationDemo = new DeSerializationDemo();
deSerializationDemo.readEmployeeObject();
}
private void readEmployeeObject() throws IOException,
FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException
{
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null;
try
{
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("employee.tmp");
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
/*
* Read an object from the ObjectInputStream.
*/
Employee employee = (Employee) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out
.println("Successfully read employee object from the file.");
System.out.println("Name = " + employee.getName());
System.out.println("Age = " + employee.getAge());
System.out.println("Salary = " + employee.getSalary());
}
finally
{
if (objectInputStream != null)
{
/*
* Closing a ObjectInputStream will also
* close the InputStream instance from which
* the ObjectInputStream is reading.
*/
objectInputStream.close();
}
}
}
}
Successfully read employee object from the file.
Name = Peter
Age = 29
Salary = 80000
No comments:
Post a Comment