Click here to watch in Youtube :
Click the below Image to Enlarge
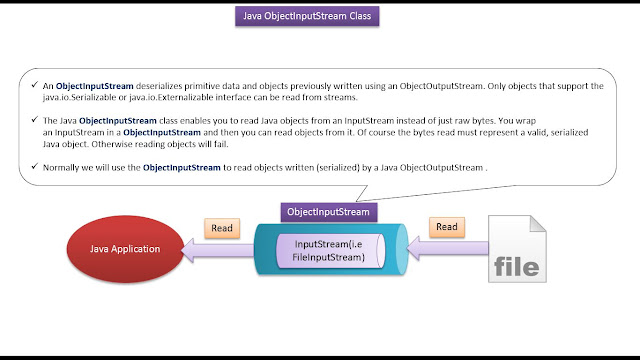 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java ObjectInputStream | Java Serialization) |
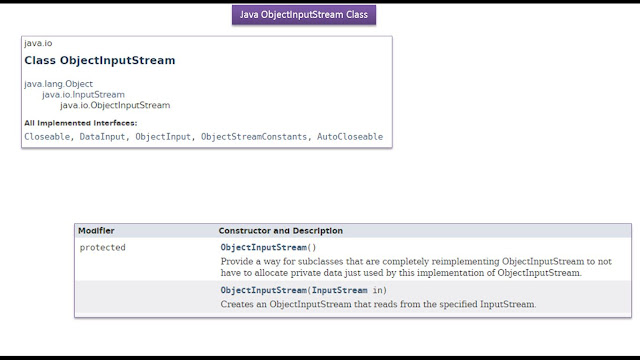 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java ObjectInputStream | Java Serialization) |
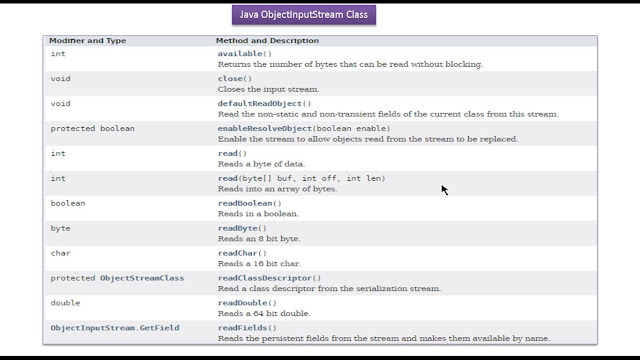 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java ObjectInputStream | Java Serialization) |
 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java ObjectInputStream | Java Serialization) |
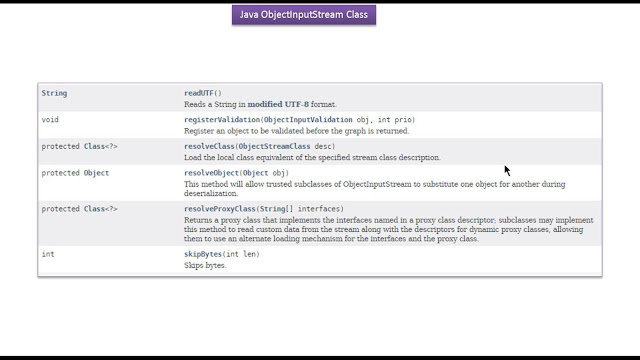 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java ObjectInputStream | Java Serialization) |
Student.javaimport java.io.Serializable;
/*
* Before you can serialize and de-serialize objects the
* class of the object must implement java.io.Serializable.
*/
public class Student implements Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1438960132000208485L;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age)
{
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
ObjectOutputStreamDemo.java import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
ObjectOutputStreamDemo objectOutputStreamDemo = new ObjectOutputStreamDemo();
objectOutputStreamDemo.writeStudentObject();
}
private void writeStudentObject() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException
{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
try
{
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("student.tmp");
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
Student student = new Student("Peter", 15);
System.out.println(student);
/*
* Write the specified object to the
* ObjectOutputStream.
*/
objectOutputStream.writeObject(student);
System.out
.println("Successfully written student object to the file.\n");
}
finally
{
if (objectOutputStream != null)
{
/*
* Closing a ObjectOutputStream will also
* close the OutputStream instance to which
* the ObjectOutputStream is writing.
*/
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
}
}
Output Student [name=Peter, age=15]
Successfully written student object to the file.
student.tmp
ObjectInputStreamDemo.java import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
ObjectInputStreamDemo objectInputStreamDemo = new ObjectInputStreamDemo();
objectInputStreamDemo.readStudentObject();
}
private void readStudentObject() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException,
ClassNotFoundException
{
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null;
try
{
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("student.tmp");
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
/*
* Read an object from the ObjectInputStream.
*/
Student student = (Student) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out
.println("Successfully read student object from the file.");
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println("Name = " + student.getName());
System.out.println("Age = " + student.getAge());
}
finally
{
if (objectInputStream != null)
{
/*
* Closing a ObjectInputStream will also
* close the InputStream instance from which
* the ObjectInputStream is reading.
*/
objectInputStream.close();
}
}
}
}
Output Successfully read student object from the file.
Student [name=Peter, age=15]
Name = Peter
Age = 15
Refer:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/index.html?java/io/ObjectInputStream.html






No comments:
Post a Comment