Click here to watch in Youtube :
Click the below Image to Enlarge
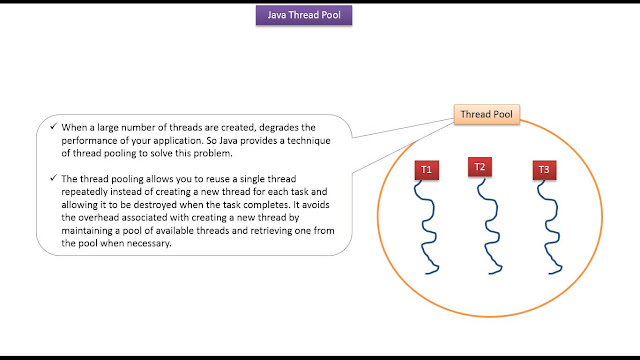 |
| Java Tutorial: Java Threads (Thread pool in java | Java thread pool | Java thread pool tutorial_V5) |
class PrintCharTask implements Runnable
{
private char character;
private int noOfTimes;
PrintCharTask(char ch, int n)
{
character = ch;
noOfTimes = n;
}
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < noOfTimes; i++)
{
System.out.println(character + " ");
}
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
class Threadpool
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Main Thread starts");
ExecutorService threadExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
PrintCharTask taskl = new PrintCharTask('*', 5);
PrintCharTask task2 = new PrintCharTask('S', 5);
PrintCharTask task3 = new PrintCharTask('M', 5);
PrintCharTask task4 = new PrintCharTask('N', 5);
threadExecutor.execute(taskl);
threadExecutor.execute(task2);
threadExecutor.execute(task3);
threadExecutor.execute(task4);
/*
* Tells the threadExecutor to shutdown. No new task
* can be accepted but the existing task will
* continue to finish.
*/
threadExecutor.shutdown();
/*
* In order to ensure that the main thread finishes
* last i.e. all tasks are finished before the main
* thread terminates, we put the below while
* statement.
*/
while (!threadExecutor.isTerminated())
{
}
System.out.println("\nMain Thread Ends");
}
}
Main Thread starts
*
*
*
*
*
M
M
M
M
M
N
N
N
N
N
S
S
S
S
S
Main Thread Ends
No comments:
Post a Comment