Modifiers in Java
Modifiers are keywords that are added to change meaning of a definition. In Java, modifiers are catagorized into two types,
- Access control modifier
- Non Access Modifier
1) Access control modifier
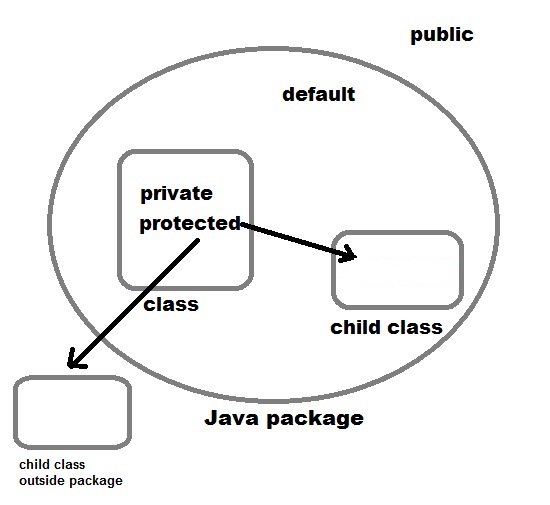
Java language has four access modifier to control access levels for classes, variable methods and constructor.
- Default : Default has scope only inside the same package
- Public : Public scope is visible everywhere
- Protected : Protected has scope within the package and all sub classes
- Private : Private has scope only within the classes
2) Non-access Modifier
Non-access modifiers do not change the accessibility of variables and methods, but they do provide them special properties. Non-access modifiers are of 5 types,
- Final
- Static
- Transient
- Synchronized
- Volatile
Final
Final modifier is used to declare a field as final i.e. it prevents its content from being modified. Final field must be initialized when it is declared.
Example :
class Cloth
{
final int MAX_PRICE = 999; //final variable
final int MIN_PRICE = 699;
final void display() //final method
{
System.out.println("Maxprice is" + MAX_PRICE );
System.out.println("Minprice is" + MIN_PRICE);
}
}
A class can also be declared as final. A class declared as final cannot be inherited. String class in java.lang package is a example of final class. Method declared as final can be inherited but you cannot override(redefine) it.
Static Modifier
Static Modifiers are used to create class variable and class methods which can be accessed without instance of a class. Lets study how it works with variables and member functions.
Static with Variables
Static variables are defined as a class member that can be accessed without any object of that class. Static variable has only one single storage. All the object of the class having static variable will have the same instance of static variable. Static variables are initialized only once.
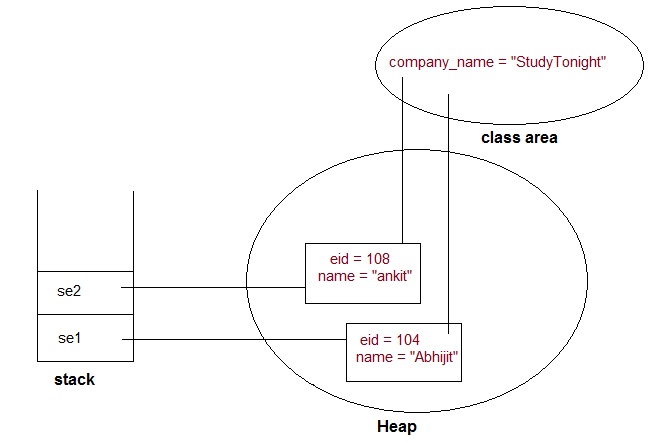
Static variable are used to represent common property of a class. It saves memory. Suppose there are 100 employee in a company. All employee have its unique name and employee id but company name will be same all 100 employee. Here company name is the common property. So if you create a class to store employee detail, company_name field will be mark as static.
Example
class Employee
{
int e_id;
String name;
static String company_name = "StudyTonight";
}
Example of static variable
class ST_Employee
{
int eid;
String name;
static String company_name ="StudyTonight";
public void show()
{
System.out.println(eid+" "+name+" "+company_name);
}
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ST_Employee se1 = new ST_Employee();
se1.eid = 104;
se1.name = "Abhijit";
se1.show();
ST_Employee se2 = new ST_Employee();
se2.eid = 108;
se2.name = "ankit";
se2.show();
}
}
Output :
104 Abhijit StudyTonight 108 ankit StudyTonight
Static variable vs Instance Variable
| Static variable | Instance Variable |
|---|---|
| Represent common property | Represent unique property |
| Accessed using class name | Accessed using object |
| get memory only once | get new memory each time a new object is created |
Example
public class Test
{
static int x = 100;
int y = 100;
public void increment()
{
x++; y++;
}
public static void main( String[] args )
{
Test t1 = new Test();
Test t2 = new Test();
t1.increment();
t2.increment();
System.out.println(t2.y);
System.out.println(Test.x); //accessed without any instance of class.
}
}
Output :
101 102
See the difference in value of two variable. Static variable y shows the changes made to it by increment() method on the different object. While instance variable x show only the change made to it by increment() method on that particular instance.
Static Method
A method can also be declared as static. Static methods do not need instance of its class for being accessed. main() method is the most common example of static method. main() method is declared as static because it is called before any object of the class is created.
Example :
class Test
{
public static void square(int x)
{
System.out.println(x*x);
}
public static void main (String[] arg)
{
square(8) //static method square () is called without any instance of class.
}
}
Output: 64Static block
Static block is used to initialize static data member. Static block executes before
main() method.
Example
class ST_Employee
{
int eid;
String name;
static String company_name;
static {
company_name ="StudyTonight"; //static block invoked before main() method
}
public void show()
{
System.out.println(eid+" "+name+" "+company_name);
}
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ST_Employee se1 = new ST_Employee();
se1.eid = 104;
se1.name = "Abhijit";
se1.show();
}
}
Output :
104 Abhijit StudyTonight
Q. Why a non-static variable cannot be referenced from a static context ?
When you try to access a non-static variable from a static context like main method, java compiler throws a message like "a non-static variable cannot be referenced from a static context". This is because non-static variables are related with instance of class(object) and they get created when instance of a class is created by using new operator. So if you try to access a non-static variable without any instance compiler will complain because those variables are not yet created and they don't have any existence until an instance is created and associated with it.
Example of accessing non-static variable from a static context
class Test
{
int x;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
x=10;
}
}
Output :
compiler error: non-static variable count cannot be referenced from a static context
Same example using instance of class
class Test
{
int x;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test tt=new Test();
tt.x=10; //works fine with instance of class
}
}
Q. Why main() method is static in java ?
Because static methods can be called without any instance of a class and main() is called before any instance of a class is created.
Transient modifier
When an instance variable is declared as transient, then its value doesn't persist when an object is serialized
Synchronized modifier
When a method is synchronized it can be accessed by only one thread at a time. We will discuss it in detail in Thread.
Volatile modifier
Volatile modifier tells the compiler that the volatile variable can be changed unexpectedly by other parts of your program. Volatile variables are used in case of multithreading program.
No comments:
Post a Comment